SAP Event Mesh Outbound
SAP Event Mesh Outbound is a test that will search for the message in SAP Event Mesh platform based on conditions specified in the Variables of Automation Object. It will check the outbound message triggered by other test case or manual action.
Top of the screen with Automation Object (AO) ID, description and test type.
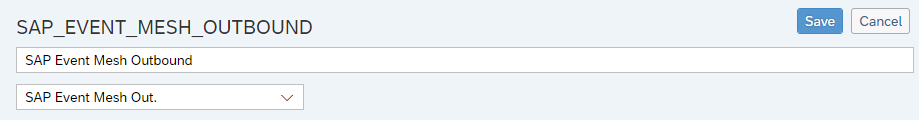
Basic Information
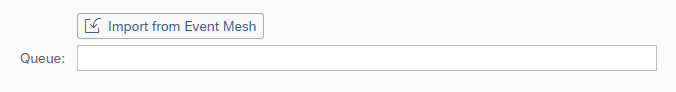
Parameter name | Description | Example |
Queue | SAP Event Mesh Queue ID | int4suite/demo/em/SalesOrderDetails |
Parameters
Parameter name | Description | Example |
SAP Event Mesh Fetch from | Fetching from Queue or Topic. Fetching from queue will read directly from the queue provided in ‘Basic Information’ section. When Fetching from Topic, program will do following:
| Queue, Topic |
SAP Event Mesh Topic Pattern | Topic name which the technical Queue will subscribe to. Value help will show Topics that selected Queue subscribes to. Applicable only if ‘Topic’ was selected in ‘SAP Event Mesh Post Fetch from' parameter. | int4suite/demo/em/ce/sap/s4/beh/salesorder/v1/SalesOrder/Created/v1 |
SAP Event Mesh Webhook | Support for webhooks will be added in next versions of Int4 Suite. | |
SAP Event Mesh Namespace | Namespace where the technical Queue for Topic testing can be created. Same as namespace of topic. Applicable only if ‘Topic’ was selected in ‘SAP Event Mesh Fetch from’ parameter. | int4suite/demo/em |
Execution Settings
In this section there are common execution settings for all test cases.
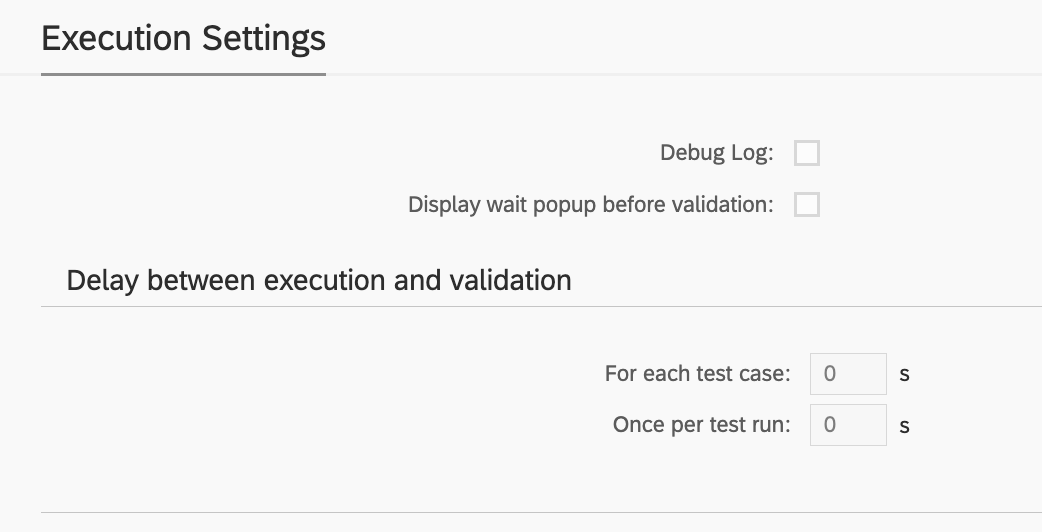
Debug Log
This feature enables additional debugging messages to be included in the test execution log. Typically, this option is disabled, as a log with debugging information can become cluttered with details unnecessary for standard test execution. However, it proves invaluable during the initial phases of working with Int4 Suite, as it provides insights into each unsuccessful run and aids in identifying and resolving connectivity and security issues.
Display Wait Popup Before Validation
In specific scenarios, there may be a need for manual intervention between the message injection by Int4 Suite and the readiness for test validation. For instance, when an XML message is injected into SAP CPI, mapped to an IDoc, and subsequently transferred to SAP S/4, the IDoc may be processed automatically by the backend. However, certain configurations could hinder this automatic processing. In such cases, the tester must log into S/4 to manually request IDoc processing. The wait popup feature facilitates this by allowing Int4 Suite to send the message and display a popup before commencing backend data validation. This gives the tester time to complete the IDoc processing, return to Int4 Suite, and confirm the popup. Only after this confirmation will Int4 Suite proceed with data validations.
Delay Between Execution and Validation
Similar to the wait popup feature, these options allow for a delay to be configured between the initiation of the test run and/or between the injection of test case data and the validation of results. If it is anticipated that backend processing or integration platform mapping may require a considerable amount of time, this section allows for the configuration of such delays. As a result, Int4 Suite will pause before attempting to validate the integration platform and/or the backend, depending on the type of test being executed.
Variables
Variables are the container for values that can be used during testing. Each variable contains two values, the one that is calculated based on the reference message/document and the one that is calculated ad-hoc during test case execution.
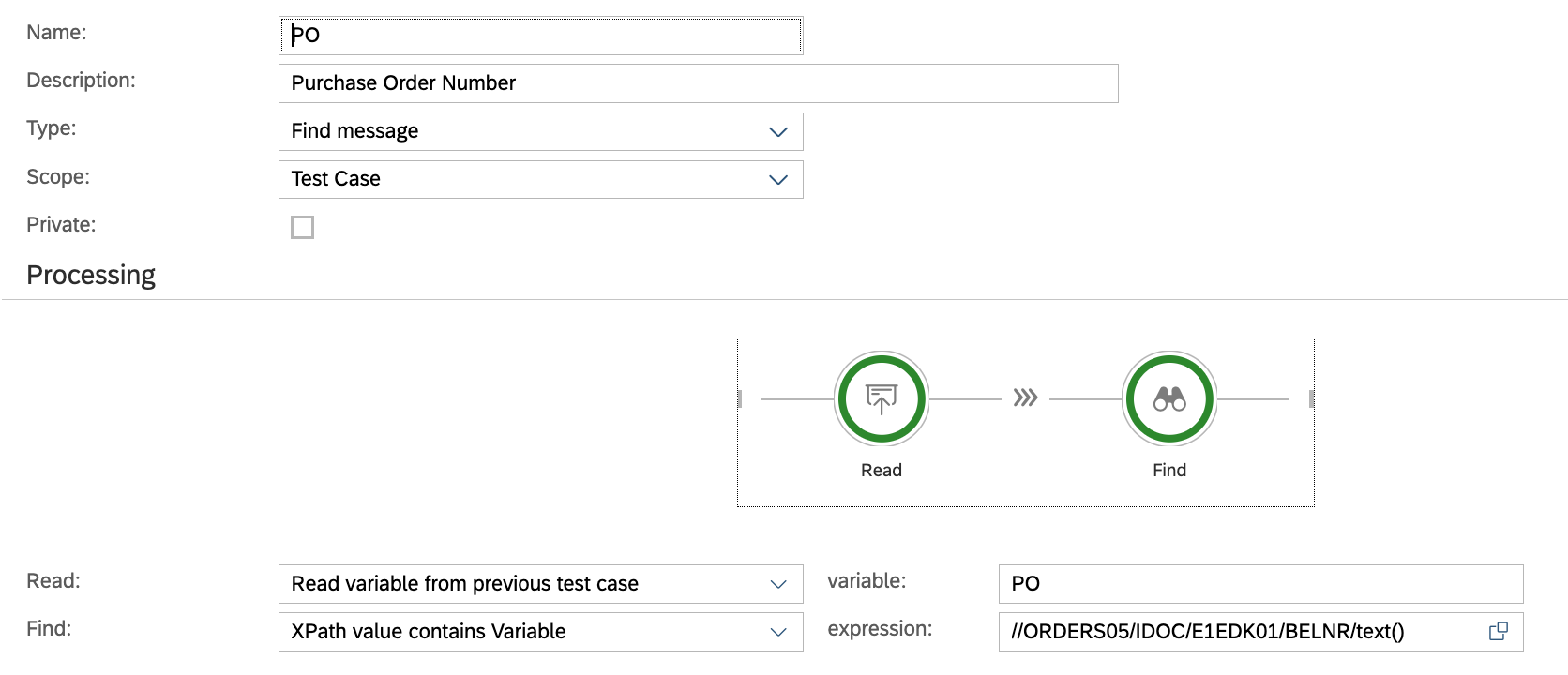
In outbound test types, variables play a crucial role in identifying the correct message leaving the system under test. The Find message type facilitates this process and consists of two steps:
Read: Specifies the value we are searching for.
Find: Indicates where the value should appear in the payload.
Apart from that there are various scenarios where variable processing can be beneficial:
Updating document/message content before test execution
Capturing data from document/message content after execution
Passing data between test cases
For more details on Variables and their processing, read here: Variables & Variable processing
Example variable definition:
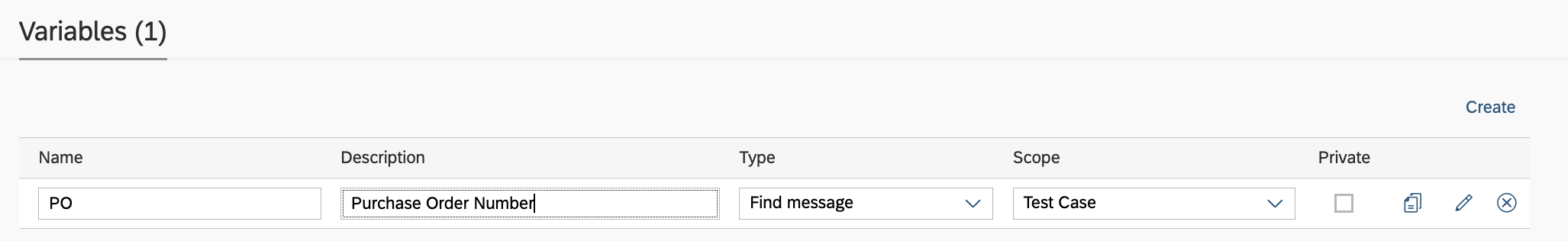
Variable details:
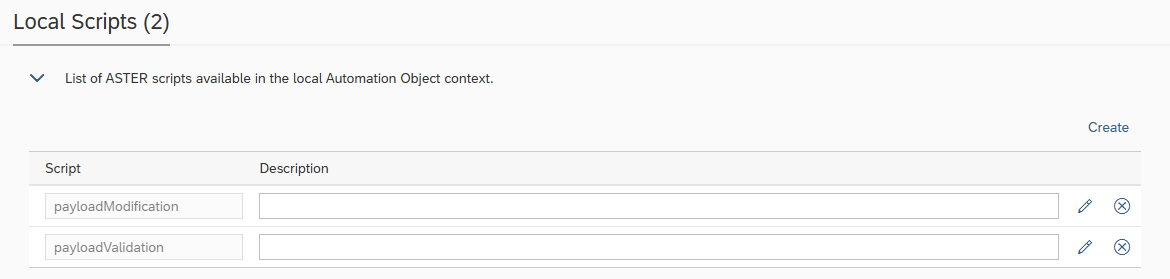
Local Scripts
Local Scripts enable you to define custom scripts that are available within the context of the current Automation Object.
These scripts can be utilized in the following areas:
Variable Processing
Payload Processing
Custom Validations
Please consult the Int4 Aster Documentation for details on the scripting language.
Payload Validations
Output payloads after processing by integration platform are validated against previously stored references.
The basic test execution in Int4 Suite will compare the messages (reference and current execution) and report any differences as errors, causing the test to fail. While this may be acceptable for some migration scenarios, not all message differences are errors; some discrepancies are even expected.
This configuration enables adding rules with exceptions that will allow for differences like document numbers, current time and date and others.
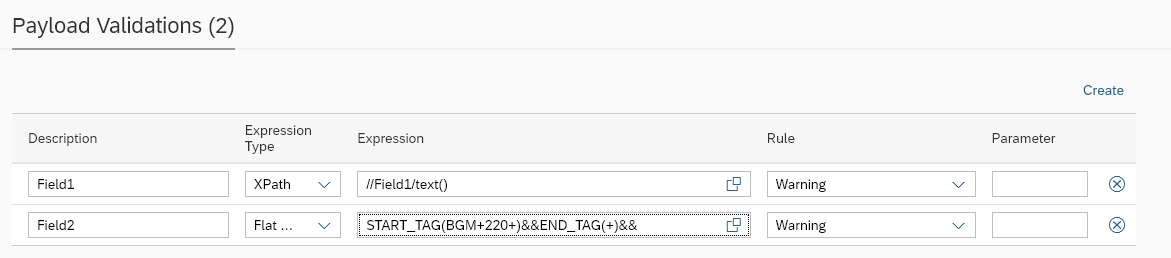
Parameter name | Description | Example |
Description | Free text for the exception rule | Field1 |
|---|---|---|
Expression Type | Expression type. Available options:
This field is optional for all interfaces where there is a single type of output. However, for interfaces that output might be both XML and flat file, it is mandatory to specify the expression type, then it would be only apply to specific file format (XML/JSON or flat file) | XPath |
Expression | Path pointing to the field/node where the exception should be applied. Available syntaxes: XPath, JSONPath, Int4 Flat File Syntax or REGEX JSONPath and XPath are well-known and popular standards for structured data manipulation. You can find a lot of references and educational material on-line. Worth noting are the testing tools that allow You to experiment with XPath or JSONPath definitions. See here: Please note that Int4 does not maintain these tools and can’t guarantee for their accuracy. | //ORDER/DATE/text() (XPATH expression) or START_TAG(BGM+220+)&&END_TAG(+)&& (Flat file expression) or |
Rule | Says how the difference should be marked
Change Request rule are active only when Test Case is run within Test Run type: Change Request Test |
|
Parameter | Additional parameter for rules |
|
Custom Validations
Custom Validations offer enhanced flexibility for evaluating test case results by allowing the implementation of custom logic using ASTER Scripts.
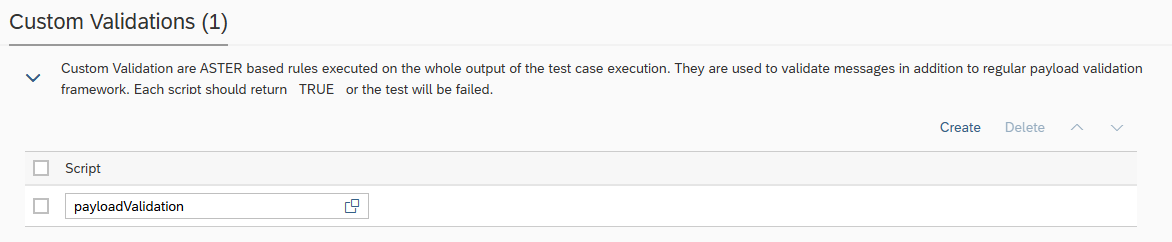
Within the script, you can access test execution data using built-in Int4 Suite functions such as:
GET_TC_VAR– to retrieve test case variablesGET_VALIDATION_PAYLOADS– to access payloads used during validation
For the test case to be marked as successful, the script must return a _TRUE_ value.
Data Scrambling
Data scrambling enables to reduce or remove GDPR, privacy and security concerns when it comes to testing. When Int4 Suite is extracting the test data from existing messages or reports testing results, the visibility and availability of sensitive data could be an issue. To avoid this issue, sensitive data can be scrambled. Scrambling can occur at test case creation time and during the test execution. Actual behaviour of the scrambling engine is configured by a set of rules.
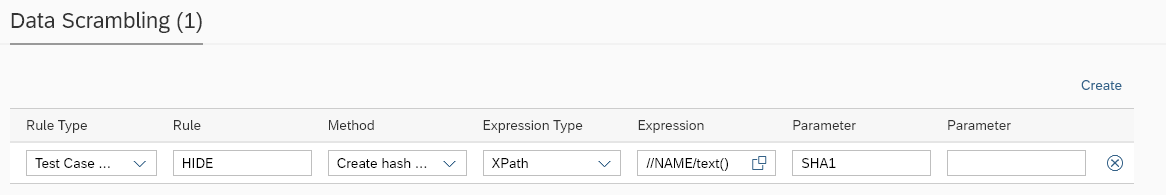
Parameter name | Description | Example |
Rule Type | Rule type. Available options:
| Test Case Creation |
|---|---|---|
Rule | Free text to specify scrambling rule name for identification. | NAME |
Method | Choose a scrambling method from a list. Available methods:
| HASH |
Expression Type | Expression type. Available options:
This field is optional for all interfaces where there is a single type of output. However, for interfaces that output might be both XML and flat file, it is mandatory to specify the expression type. | XPath |
Expression | Path pointing to the field/node where the exception should be applied. | //ORDER/DATE/text() (XPATH expression) or START_TAG(BGM+220+)&&END_TAG(+)&& (Flat file expression) or $.order.date (JSONPath expression) or REGEX(BGM\+220\+(.*)\+) (REGEX expression) |
Parameter | Specify Additional Parameter suitable for a chosen scrambling method like X (for Mask method), SHA1 (for HASH Method) |
